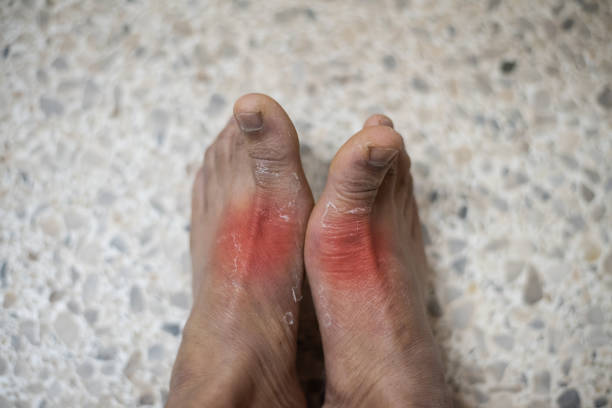
Diabetes is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While most people know about its impact on blood sugar levels, not everyone realizes how it can affect the feet. Diabetic foot problems are common and can lead to severe complications if not properly managed. High blood sugar can cause nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation, making it harder to feel injuries and slowing down the healing process. This combination increases the risk of infections, ulcers, and, in extreme cases, amputation.
Taking care of your feet is an essential part of diabetes management. In this guide, we will discuss why foot care is crucial, how to prevent diabetic foot problems, and what to do if complications arise.
Why Foot Care Is Important for People with Diabetes
Diabetes can lead to two major issues that affect the feet:
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves in your feet, reducing sensation. This means you may not feel pain from minor cuts, blisters, or injuries, increasing the risk of infections.
- Poor Circulation: Diabetes can cause blood vessels to narrow and harden, reducing blood flow to the feet. Poor circulation slows down healing and makes infections more difficult to fight off.
Without proper care, even a small cut can turn into a serious problem. That’s why daily foot care and regular checkups are vital.
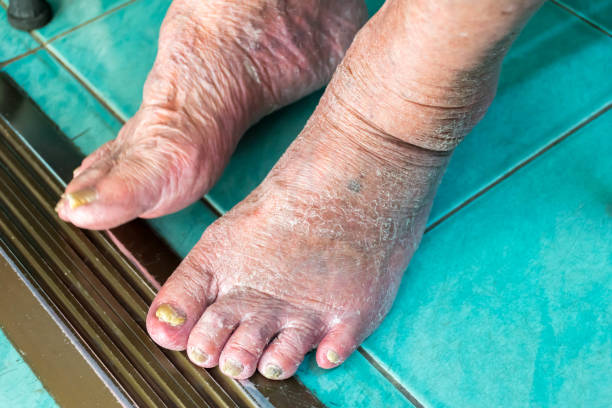
How to Prevent Diabetic Foot Problems
Taking a proactive approach to foot care can help prevent serious complications. Follow these essential steps to keep your feet healthy:
1. Inspect Your Feet Daily
Make it a habit to check your feet every day for any cuts, sores, blisters, redness, swelling, or signs of infection. Catching these issues early can help prevent complications. If you have trouble seeing the bottoms of your feet, use a mirror or ask a family member for assistance. Pay special attention to areas between the toes and around the heels, where problems can develop unnoticed.
If you notice any wounds, discoloration, or unusual changes, contact your doctor immediately for proper care. Regular foot inspections are essential for maintaining healthy feet and preventing serious issues.
2. Wash Your Feet with Care
Keeping your feet clean is essential for preventing infections and maintaining overall foot health. Wash your feet daily using warm (not hot) water and a mild soap to remove dirt, sweat, and bacteria. Avoid soaking them for long periods, as this can strip away natural oils and lead to dryness or cracking.
After washing, dry your feet thoroughly, paying special attention to the areas between your toes, as moisture buildup can create the perfect environment for fungal infections. For extra protection, consider applying a fragrance-free moisturizer to keep your skin soft, but avoid putting lotion between the toes to prevent excess moisture.
3. Keep Your Skin Moisturized
Diabetes and other conditions can lead to dry, cracked skin on the feet, increasing the risk of infections. To keep your skin soft and healthy, apply a fragrance-free moisturizer to the tops and bottoms of your feet daily. Well-hydrated skin is less likely to crack, reducing the chances of bacteria entering and causing complications. However, avoid applying lotion between your toes, as trapped moisture can create an ideal environment for fungal infections.
If you notice persistent dryness, peeling, or irritation, consult your doctor for recommendations on the best foot care routine. Keeping your skin properly moisturized is a simple but crucial step in maintaining overall foot health.
4. Wear Proper Footwear
Wearing the right shoes is essential for maintaining foot health and preventing common issues like blisters, pressure sores, and foot pain. Choose well-fitted, comfortable shoes that provide adequate support, cushioning, and protection. Avoid tight shoes, high heels, or styles with pointed toes, as they can create pressure points and increase the risk of foot injuries.
Always wear moisture-wicking socks to reduce friction, prevent blisters, and protect your feet from cuts or infections. If you have diabetes or other foot concerns, consider shoes designed specifically for extra support and protection. Prioritizing proper footwear can help keep your feet healthy and pain-free in the long run.
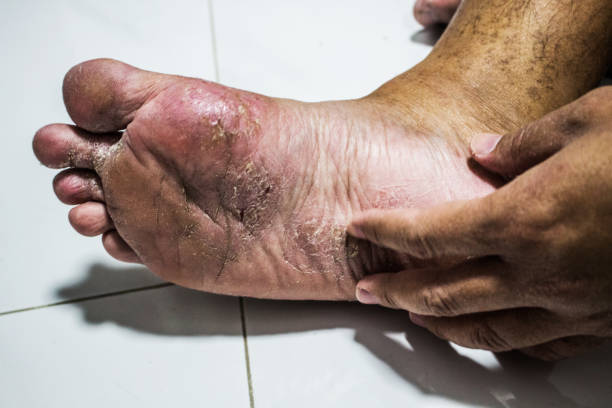
5. Trim Your Toenails Properly
Proper toenail care is essential for preventing painful conditions like ingrown toenails and infections. Always trim your toenails straight across rather than rounding the edges, as this helps reduce the risk of the nail growing into the skin. Avoid cutting them too short, as this can cause discomfort and increase the chances of irritation. Use clean, sharp nail clippers and gently file any rough edges to prevent snags.
If you have difficulty trimming your nails due to mobility issues, thickened nails, or diabetes, consider visiting a podiatrist for professional nail care. Keeping your toenails properly trimmed helps maintain healthy feet and prevents complications.
6. Manage Your Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and plays a key role in preventing foot problems, especially for people with diabetes. High blood sugar can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation, increasing the risk of infections, slow-healing wounds, and foot ulcers. To keep your blood sugar within the recommended range, follow your doctor’s guidance on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and prescribed medications.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels consistently can help you detect any fluctuations early and take corrective action. By managing your diabetes effectively, you can protect your feet from serious complications and maintain long-term foot health.
7. Avoid Walking Barefoot
Protecting your feet from injury is essential, especially if you have diabetes or reduced sensation due to neuropathy. Always wear well-fitted shoes, slippers, or protective footwear, even when indoors, to reduce the risk of cuts, scrapes, or puncture wounds. Walking barefoot increases the chances of stepping on sharp objects, such as glass, nails, or small debris, which can cause injuries that may go unnoticed if you have nerve damage.
Even minor wounds can lead to infections or complications if left untreated. By wearing proper footwear at all times, you can safeguard your feet and prevent unnecessary injuries.
8. Schedule Regular Foot Checkups
Routine foot checkups with a podiatrist or healthcare provider are essential for early detection and prevention of foot-related complications. Regular examinations can help identify issues such as poor circulation, nerve damage, infections, or deformities before they become serious problems. Your doctor can also provide professional care, including toenail trimming, callus removal, and personalized foot care advice.
If you have diabetes or other conditions affecting your feet, scheduling checkups at least once a year—or more frequently if recommended—can help prevent long-term complications. Prioritizing regular foot care appointments ensures your feet stay healthy and reduces the risk of serious issues down the road.
How to Treat Diabetic Foot Problems
Despite your best efforts, foot problems can still occur. If you notice a wound or infection, it’s essential to act quickly. Here’s what to do:
Treating Minor Cuts and Sores
- Clean the Area: Gently wash the wound with mild soap and water.
- Apply an Antibiotic Ointment: This helps prevent infections.
- Cover the Wound: Use a clean bandage to protect it from bacteria.
- Avoid Putting Pressure on the Affected Area: Try to keep weight off the injured foot.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: If redness, swelling, pus, or increasing pain develops, contact your doctor immediately.
When to Seek Medical Help
If a wound doesn’t start to heal within a few days or gets worse, see a doctor as soon as possible. You should also seek immediate medical care if you notice any of the following:
- Skin discoloration (blue, black, or red patches)
- A wound that oozes pus or has a foul smell
- Severe pain, numbness, or tingling
- Fever or other signs of infection
Doctors may prescribe antibiotics, special dressings, or other treatments to help heal the wound. In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove infected tissue.
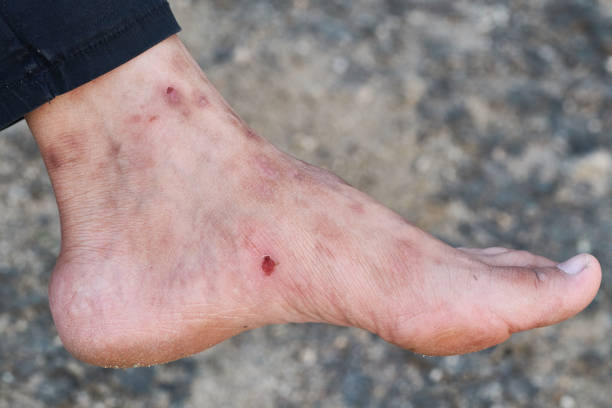
The Importance of Early Intervention
Ignoring diabetic foot problems can lead to severe complications, including infections, foot ulcers, and, in extreme cases, amputations. However, early intervention significantly reduces these risks and helps maintain overall foot health. Research shows that proper foot care can lower the risk of foot ulcers by up to 85%, making prevention a crucial part of diabetes management.
Simple habits like daily foot inspections, maintaining good hygiene, wearing proper footwear, and scheduling regular checkups with a podiatrist can make a major difference. By taking proactive steps, you can prevent serious foot issues and protect your long-term mobility and quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Diabetic foot problems are common, but the good news is that they are largely preventable with the right care and attention. By practicing good foot hygiene, wearing properly fitted footwear, keeping your skin moisturized, and managing your blood sugar levels, you can significantly reduce the risk of infections, ulcers, and other complications. Regular foot inspections and routine checkups with a healthcare provider can help catch potential issues early before they become serious.
If you notice any wounds, redness, swelling, or unusual changes in your feet, don’t ignore them—seek medical attention immediately. Early intervention can make all the difference in preventing long-term damage.
By prioritizing foot care, you can stay active, independent, and free from painful foot conditions. Your feet support you every day—give them the care they deserve!