Diabetes affects millions of people worldwide, impacting more than just blood sugar levels—it can also lead to various skin problems. In fact, skin issues are often one of the first warning signs of diabetes. High blood sugar can cause dryness, irritation, infections, and slow wound healing, making proper skin care essential for those managing diabetes. The good news is that with the right skincare routine and preventive measures, many of these issues can be avoided.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most common diabetes-related skin conditions and provide expert tips to help you keep your skin healthy, hydrated, and protected.
Why Does Diabetes Affect the Skin?
Diabetes can have a significant impact on skin health, primarily due to high blood sugar levels. When blood sugar is too high, the body loses fluids, leading to dehydration and dry, itchy skin. Cracked skin can create openings for bacteria, increasing the risk of infections. Additionally, diabetes weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and heal wounds properly.
Poor circulation further slows the healing process, raising the risk of sores and ulcers, especially on the feet and legs. The good news is that by keeping blood sugar levels under control and following a proper skincare routine, you can reduce the likelihood of these complications and keep your skin healthy.
Common Skin Problems Caused by Diabetes and How to Prevent Them
Diabetes can lead to several skin conditions, often as a result of high blood sugar, poor circulation, and a weakened immune system. Below are some of the most common diabetes-related skin issues and expert tips on how to prevent them.
1. Dry and Itchy Skin
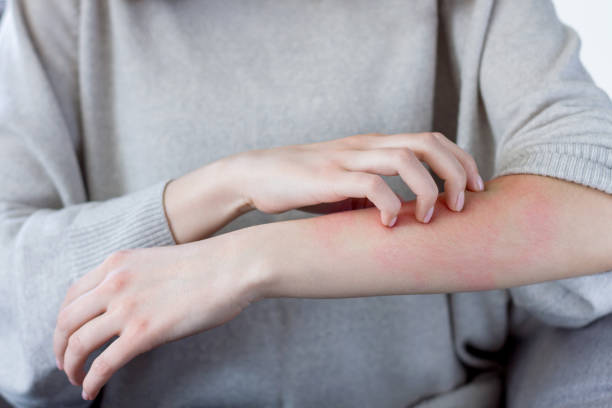

High blood sugar pulls moisture from the skin, leading to dryness and itchiness. Scratching dry skin can cause breaks, making it easier for bacteria to enter and cause infections.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer daily.
- Take lukewarm showers instead of hot ones to prevent further drying.
- Use a humidifier at home to maintain moisture levels in the air.
2. Fungal Infections
People with diabetes are more prone to fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, jock itch, and yeast infections. These thrive in warm, moist areas like the armpits, under the breasts, and between the toes.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Keep skin clean and dry, especially in folds and creases.
- Wear loose, breathable clothing to prevent excessive sweating.
- Use antifungal powders or creams as needed.
- Change socks and underwear daily to reduce moisture buildup.
3. Bacterial Infections
Diabetes increases the risk of bacterial infections such as boils, styes, and infected hair follicles. These infections often cause redness, swelling, and pain.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Wash your hands frequently to prevent bacterial spread.
- Clean any cuts or scrapes immediately and apply antibiotic ointment.
- Avoid picking at pimples, boils, or other skin irritations.
- Seek medical care if an infection worsens or doesn’t heal within a few days.
4. Slow-Healing Wounds
High blood sugar can damage blood vessels, slowing down the healing process. Untreated wounds may become infected, increasing the risk of ulcers and serious complications.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Inspect your skin daily for cuts, blisters, or sores, especially on your feet.
- Keep wounds clean and covered to prevent infections.
- Wear properly fitting shoes to reduce friction and blisters.
- See a doctor for wounds that do not heal within a week.
5. Diabetic Dermopathy
This condition causes light brown, scaly patches on the legs. While harmless, it can indicate poor circulation and should not be ignored.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Keep blood sugar levels well-managed to reduce skin damage.
- Apply moisturizer to affected areas to prevent dryness.
- Protect your skin from injury to avoid worsening symptoms.
6. Acanthosis Nigricans
This condition leads to dark, thickened patches of skin, often in body folds such as the neck, armpits, and groin. It is usually linked to insulin resistance.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Keep the affected areas clean and dry.
- Consult a doctor about possible treatments, such as topical creams or laser therapy.
7. Diabetic Blisters
Some people with diabetes develop painless blisters on their hands, feet, or legs. While these blisters usually heal on their own, they can become infected if not properly cared for.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- Keep blood sugar levels under control to prevent blisters.
- Wear comfortable, well-fitted shoes to minimize friction.
- Avoid popping blisters, as this can lead to infection.
By staying proactive with your skincare routine and keeping your blood sugar in check, you can significantly lower your risk of diabetes-related skin conditions. If you notice persistent skin issues, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Essential Skin Care Tips for People with Diabetes
Maintaining a proper skincare routine is key to preventing diabetes-related skin issues. In addition to targeting specific conditions, following general skin care habits can help keep your skin healthy, hydrated, and infection-free.
1. Keep Your Skin Clean and Moisturized
Proper cleansing and hydration are essential to maintaining skin health and preventing dryness, irritation, and infections.
✅ Best Practices:
- Wash with a mild, fragrance-free soap and warm (not hot) water to prevent skin irritation.
- Pat your skin dry gently with a soft towel instead of rubbing.
- Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer immediately after bathing to lock in moisture and prevent dryness.
2. Protect Your Feet
Diabetes increases the risk of foot problems, including infections and ulcers. Taking extra care of your feet can prevent serious complications.
✅ Best Practices:
- Inspect your feet daily for cuts, sores, blisters, or signs of infection.
- Trim toenails carefully to avoid ingrown nails and infections.
- Wear well-fitted, supportive shoes to prevent pressure sores and blisters.
- Avoid walking barefoot, even indoors, to reduce the risk of injuries.
3. Manage Blood Sugar Levels
One of the best ways to protect your skin is by keeping your blood sugar levels in check. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to dry skin, slow healing, and increased infection risks.
✅ Best Practices:
- Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and promote overall skin health.
- Take prescribed diabetes medications as directed by your doctor.
4. Seek Medical Attention for Skin Issues
Early intervention is crucial in preventing minor skin problems from becoming serious infections or ulcers.
✅ When to See a Doctor:
- Persistent redness, swelling, or pain
- Wounds that do not heal
- Frequent skin infections or rashes
- Severe itching or thickened skin patches
By following these general skin care tips and maintaining good diabetes management, you can significantly reduce your risk of skin complications. If you notice any unusual skin changes, consult your doctor for early treatment and personalized care.

Conclusion: Keeping Your Skin Healthy with Diabetes
Diabetes can lead to various skin problems, but with the right care and preventive measures, you can keep your skin healthy and reduce the risk of complications. A consistent skincare routine—including proper cleansing, moisturizing, and protection—can help prevent dryness, infections, and slow-healing wounds.
Managing blood sugar levels is just as important, as high glucose levels contribute to many diabetes-related skin conditions. Regularly inspect your skin, especially your feet, for any cuts, sores, or unusual changes. Early detection and treatment of skin issues can prevent minor problems from turning into serious health concerns.
By staying proactive with your skincare routine, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking medical attention when needed, you can maintain healthy skin and improve your overall well-being while managing diabetes.