Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to various health complications. One of the most common and serious complications is diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels. This condition can result in pain, tingling, numbness, and even loss of sensation, particularly in the hands and feet.
If left untreated, it can lead to severe issues, including infections and mobility problems. Understanding diabetic neuropathy—how it develops, its symptoms, and the best ways to manage or prevent it—is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life with diabetes.
What Is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves over time. This condition can affect various parts of the body, but it most commonly impacts the legs and feet, leading to pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness. If left unmanaged, diabetic neuropathy can result in severe complications, including infections, ulcers, and even amputation.
There are four main types of diabetic neuropathy, each affecting different areas of the body:
- Peripheral Neuropathy – The most common type, affecting the hands, feet, legs, and arms. Symptoms include pain, burning sensations, and loss of feeling.
- Autonomic Neuropathy – This affects the nerves that control internal organs, impacting functions like heart rate, digestion, bladder control, and blood pressure regulation.
- Proximal Neuropathy – This type primarily affects the hips, thighs, and buttocks, leading to muscle weakness, severe pain, and difficulty with movement.
- Focal Neuropathy – A sudden, isolated nerve damage that can occur in the head, torso, or legs, causing sharp pain or weakness in specific areas.
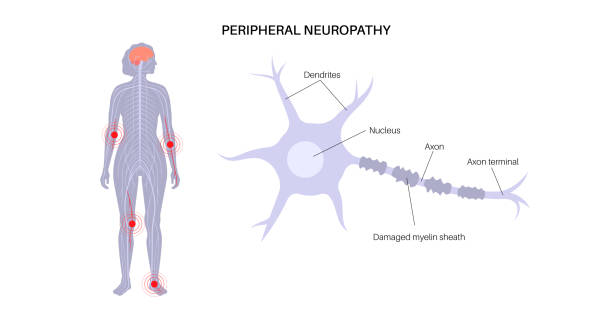
Understanding the different types of diabetic neuropathy is crucial for early detection and proper management. By keeping blood sugar levels under control and following a proactive care plan, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of nerve damage and maintain a better quality of life.
Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy symptoms can vary based on the type of nerve damage and the affected area of the body. Some people may experience mild symptoms, while others may develop severe pain or loss of sensation. Recognizing the early signs of neuropathy can help prevent complications and improve management.
The most common symptoms of diabetic neuropathy include:
- Numbness or tingling in the hands, feet, or legs, which may worsen over time
- Burning, sharp, or stabbing pain, especially at night
- Muscle weakness or loss of coordination, making it harder to walk or perform daily tasks
- Increased sensitivity to touch, where even light contact causes discomfort
- Digestive issues, such as bloating, nausea, constipation, or diarrhea
- Dizziness or fainting due to blood pressure fluctuations, which can increase the risk of falls
- Bladder problems, including difficulty controlling urination or frequent infections
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to speak with your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and proper management, including blood sugar control, lifestyle changes, and medications, can help slow the progression of diabetic neuropathy and reduce complications.speak with your doctor as soon as possible.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy develops when high blood sugar levels damage nerves over time, leading to pain, numbness, and other complications. While prolonged uncontrolled diabetes is the primary cause, several other factors can increase the risk of developing nerve damage.
Key Causes and Risk Factors:
- Poor Blood Sugar Control – Consistently high blood sugar levels damage nerves and the blood vessels that supply them, increasing the risk of neuropathy. Keeping blood sugar within a healthy range is crucial for prevention.
- Duration of Diabetes – The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing nerve damage. Neuropathy is more common in those who have had diabetes for many years.
- High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol – These conditions can harm blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the nerves, making them more vulnerable to damage.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use – Smoking restricts blood flow to the nerves, while excessive alcohol use can worsen nerve damage and lead to additional complications.
- Obesity – Being overweight increases insulin resistance and inflammation, both of which contribute to nerve damage and worsen diabetes-related complications.
Managing these risk factors through a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, proper nutrition, and medication can significantly reduce the chances of developing diabetic neuropathy. Taking proactive steps early on can help protect nerve health and improve overall well-being.
How Is Diabetic Neuropathy Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose diabetic neuropathy through a physical exam and medical history. They may perform tests such as:
- Nerve Function Tests – These measure how well nerves are working.
- Electromyography (EMG) – This checks electrical activity in muscles.
- Nerve Biopsy – In rare cases, a small sample of nerve tissue is taken for testing.
- Blood Tests – These help rule out other causes of nerve problems.
Treatment and Management of Diabetic Neuropathy
While there is no cure for diabetic neuropathy, proper treatment can help manage symptoms, slow progression, and prevent further nerve damage. A combination of blood sugar control, medications, lifestyle changes, and foot care can significantly improve quality of life for those with diabetes.
1. Blood Sugar Control

Keeping blood sugar levels stable is the most important step in managing diabetic neuropathy. High blood sugar damages nerves, so maintaining healthy glucose levels can help slow nerve deterioration and relieve symptoms. Doctors typically recommend:
- A balanced diet with low sugar intake
- Regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity
- Medications or insulin therapy as needed
2. Medications for Pain Relief
Although nerve damage cannot be reversed, certain medications can help reduce pain and discomfort associated with diabetic neuropathy, including:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Prescription medications, like anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin) or antidepressants (amitriptyline, duloxetine)
- Topical treatments, such as capsaicin cream or lidocaine patches
3. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthy habits can help protect nerves and reduce symptoms:
- Eating a nutrient-rich diet with plenty of vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Exercising regularly to improve circulation and manage blood sugar levels
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol, as both can worsen nerve damage
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol to protect blood vessels and nerves
4. Foot Care
Diabetic neuropathy commonly affects the feet, increasing the risk of infections, ulcers, and even amputation. Proper daily foot care is essential:
- Check feet daily for cuts, blisters, or sores
- Keep feet clean and dry to prevent infections
- Wear well-fitting, cushioned shoes to protect sensitive areas
- Schedule regular foot exams with a healthcare provider
By managing blood sugar, making lifestyle changes, and practicing good foot care, individuals with diabetic neuropathy can reduce complications and improve their overall well-being. If symptoms worsen, consulting a doctor for personalized treatment options is essential.
Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy
The best way to prevent diabetic neuropathy is by effectively managing diabetes and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Long-term high blood sugar damages nerves, so taking proactive steps early can significantly reduce the risk of developing nerve damage.
Key Strategies for Preventing Diabetic Neuropathy:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Keeping blood sugar within a healthy range is essential. Frequent monitoring allows for better control and helps prevent long-term complications. Your doctor may recommend:
- Using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) or a blood glucose meter
- Keeping a blood sugar log to track patterns and make necessary adjustments
- Following an individualized target range for blood sugar levels
2. Follow a Diabetes-Friendly Diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in preventing diabetic neuropathy. Focus on:
- High-fiber foods like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
- Lean proteins such as fish, poultry, and legumes
- Healthy fats like nuts, seeds, and olive oil
- Avoiding processed foods, excess sugar, and refined carbs to prevent blood sugar spikes
3. Exercise Consistently

Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, circulation, and nerve health. Try to:
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week (e.g., walking, swimming, cycling)
- Incorporate strength training to maintain muscle function and support nerve health
- Stay physically active throughout the day to prevent blood sugar fluctuations
4. Take Prescribed Medications as Directed
If your doctor has prescribed diabetes medications or insulin, taking them as instructed is crucial for blood sugar management. Skipping doses or inconsistent use can increase the risk of nerve damage and other complications.
5. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Smoking restricts blood flow to the nerves, increasing the risk of neuropathy
- Excess alcohol can contribute to nerve damage and make blood sugar levels harder to control
6. Schedule Regular Doctor Checkups
Routine checkups with your healthcare provider help detect early signs of neuropathy and prevent complications. During visits, your doctor may:
- Check nerve function and sensitivity
- Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Provide personalized recommendations for diabetes management
By staying proactive with diabetes care, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can greatly reduce the risk of developing diabetic neuropathy and protect your long-term nerve health.
Conclusion
Diabetic neuropathy is a serious and potentially debilitating complication of diabetes that can lead to pain, numbness, and other long-term health issues. However, with proper management, lifestyle changes, and early intervention, you can slow its progression, reduce symptoms, and improve your overall well-being.
The key to preventing or managing diabetic neuropathy is keeping blood sugar levels stable, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and staying proactive with medical care. Regular exercise, a diabetes-friendly diet, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help protect your nerves and reduce complications.
If you have diabetes, it’s essential to stay informed and take action to safeguard your nerve health. Routine checkups, proper foot care, and open communication with your doctor can help you manage symptoms effectively. If you experience signs of diabetic neuropathy, such as tingling, pain, or numbness, don’t ignore them—speak with your doctor immediately to explore treatment options and prevent further damage.
By taking early and consistent steps, you can live a healthier, more comfortable life with diabetes while reducing the risk of nerve-related complications.

