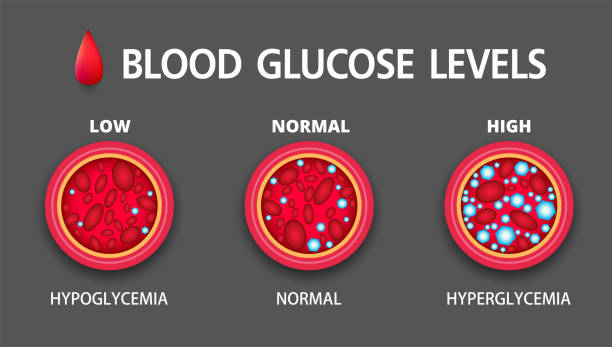
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, is a serious health concern that can have long-term effects on your body. When blood sugar levels remain elevated for an extended period, they can cause significant damage to vital organs. Three of the most vulnerable areas are the eyes, heart, and kidneys, which rely on healthy blood flow and proper function to work effectively. If left untreated, high blood sugar can lead to vision loss, heart disease, and kidney failure, increasing the risk of severe complications.
Understanding how hyperglycemia affects these organs is crucial for managing your health and preventing long-term damage. In this article, we’ll explore the connection between high blood sugar and organ damage, common symptoms to watch for, and essential steps to protect your well-being.
How High Blood Sugar Affects Your Eyes

Your eyes are highly sensitive to changes in blood sugar levels, making them one of the first areas affected by uncontrolled hyperglycemia. When blood sugar stays too high for too long, it can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to a serious condition known as diabetic retinopathy. This progressive eye disease is one of the leading causes of blindness in adults and often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages.
Signs and Symptoms of High Blood Sugar in the Eyes
If high blood sugar is affecting your eyes, you may experience:
- Blurry vision – Difficulty focusing due to fluid imbalances in the eye.
- Trouble seeing at night – Reduced night vision or difficulty adjusting to darkness.
- Floaters – Dark spots, lines, or cobweb-like shapes in your vision.
- Eye pain or pressure – A sign of increased fluid buildup or nerve damage.
- Sudden vision loss – A serious warning sign that requires immediate medical attention.
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule an eye exam with an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
Other Eye Problems Caused by High Blood Sugar
In addition to diabetic retinopathy, uncontrolled high blood sugar can increase the risk of other vision-threatening conditions, including:
- Cataracts – A clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to blurry or dim vision. People with diabetes tend to develop cataracts earlier than those without the condition.
- Glaucoma – Increased pressure inside the eye, which can damage the optic nerve and cause permanent vision loss if left untreated.
How to Protect Your Vision from High Blood Sugar
To keep your eyes healthy and reduce the risk of diabetes-related vision problems:
✔ Control your blood sugar levels through a balanced diet, exercise, and medication if needed.
✔ Schedule regular eye exams to catch problems early before they worsen.
✔ Manage blood pressure and cholesterol, as these also contribute to eye damage.
✔ Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from harmful UV rays, which can worsen cataracts.
By taking proactive steps to manage your blood sugar and overall eye health, you can reduce the risk of vision loss and protect your sight for years to come.
How High Blood Sugar Affects Your Heart
Your heart and blood vessels play a crucial role in maintaining overall health, but high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can put them at serious risk. When blood sugar levels remain elevated over time, they contribute to heart disease, high blood pressure, and poor circulation. In fact, heart disease is the leading cause of death for individuals with diabetes, making blood sugar control essential for cardiovascular health.
How High Blood Sugar Harms the Heart
Uncontrolled blood sugar affects the heart in several ways:
✔ Increases Blood Pressure – High blood sugar causes blood vessels to become stiff and narrow, leading to hypertension (high blood pressure), which forces the heart to work harder.
✔ Raises Bad Cholesterol – Diabetes lowers “good” HDL cholesterol while increasing “bad” LDL cholesterol. This imbalance can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis), increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
✔ Causes Inflammation – Chronic high blood sugar triggers inflammation, which can damage blood vessels and the heart over time, leading to cardiovascular complications.
Symptoms of Heart Problems from High Blood Sugar
People with high blood sugar or diabetes should be aware of the following heart-related warning signs:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Irregular heartbeat (palpitations or skipped beats)
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately, as they could indicate serious heart issues such as a heart attack, heart failure, or poor circulation.
Ways to Protect Your Heart from High Blood Sugar
Taking proactive steps to manage blood sugar can greatly reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are some key ways to keep your heart healthy:
✔ Follow a Heart-Healthy Diet – Eat a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods and refined sugars.
✔ Exercise Regularly – Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise (such as walking, cycling, or swimming) most days of the week to improve circulation and strengthen the heart.
✔ Monitor Blood Sugar, Blood Pressure, and Cholesterol – Regular check-ups and monitoring help catch potential problems early. Keep your A1C, cholesterol, and blood pressure within a healthy range.
✔ Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol – Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease, while excessive alcohol consumption can lead to blood sugar spikes and high blood pressure.
By managing your blood sugar effectively, you can protect your heart, reduce the risk of complications, and live a healthier life. Small lifestyle changes today can make a big difference in your long-term heart health.
How High Blood Sugar Affects Your Kidneys
Your kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste and excess fluids from your blood, helping to keep your body healthy. However, high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can put a serious strain on kidney function, leading to long-term damage. When blood sugar levels remain elevated, they damage the tiny blood vessels (glomeruli) in the kidneys, making it harder for them to filter waste properly. Over time, this condition—known as diabetic nephropathy (diabetic kidney disease)—can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Damage from High Blood Sugar
Kidney disease often progresses without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, making regular check-ups essential. As the condition worsens, you may experience:
✔ Swelling in the feet, ankles, or hands – Caused by fluid retention due to poor kidney function.
✔ Trouble urinating – Changes in urination, such as decreased output or difficulty urinating.
✔ Foamy or bloody urine – Foam may indicate excess protein in the urine (proteinuria), while blood can be a sign of kidney damage.
✔ High blood pressure – Damaged kidneys struggle to regulate blood pressure, leading to hypertension, which further worsens kidney function.
✔ Fatigue and weakness – The buildup of toxins in the body can cause tiredness and reduced energy levels.
If kidney disease progresses to kidney failure, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be required to replace lost kidney function.
Ways to Protect Your Kidneys from High Blood Sugar
Protecting your kidneys starts with managing blood sugar levels and making healthy lifestyle choices. Here’s how:
✔ Keep Your Blood Sugar in a Healthy Range – Regularly monitor and manage your blood sugar levels to reduce strain on the kidneys.
✔ Stay Hydrated – Drinking plenty of water helps the kidneys flush out toxins and function efficiently.
✔ Reduce Salt and Processed Foods – A low-sodium diet helps prevent high blood pressure, which can worsen kidney damage.
✔ Monitor Kidney Function Regularly – Get routine kidney function tests (such as eGFR and urine protein tests) to detect any early signs of damage.
✔ Maintain a Healthy Blood Pressure – High blood pressure accelerates kidney disease, so aim to keep it below 130/80 mmHg.
✔ Exercise Regularly – Physical activity helps regulate blood sugar, blood pressure, and overall kidney health.
By taking proactive steps to control blood sugar and maintain kidney health, you can lower your risk of diabetic kidney disease and prevent serious complications. Early detection and lifestyle changes can help preserve kidney function and improve long-term well-being.
Preventing Organ Damage from High Blood Sugar
The best way to protect your eyes, heart, and kidneys from high blood sugar is through proper diabetes management and a healthy lifestyle. Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to serious complications, but with the right steps, you can reduce your risk and maintain overall health.
Key Steps to Prevent Organ Damage from High Blood Sugar
✔ Check Your Blood Sugar Regularly – Monitor your blood sugar levels throughout the day and take action if they become too high. Keeping your A1C levels in a healthy range (typically below 7%) can significantly lower your risk of complications.
✔ Follow a Balanced, Blood-Sugar-Friendly Diet – Eat a nutrient-rich diet that includes:
- Whole grains (such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats) for slow-digesting carbohydrates.
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes) to support muscle health.
- Plenty of vegetables for essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Healthy fats (like avocados, nuts, and olive oil) to reduce inflammation.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbs, which can cause blood sugar spikes.
✔ Exercise Daily – Regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels, improve circulation, and strengthen the heart. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise (like walking, cycling, or swimming) most days of the week.
✔ Take Medications as Prescribed – If your doctor prescribes insulin or other diabetes medications, take them as directed to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent long-term complications.
✔ See Your Doctor Regularly – Routine medical check-ups and screenings help catch problems early, before they become severe. Make sure to schedule:
- Eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy and other vision issues.
- Heart health screenings to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and cardiovascular risk.
- Kidney function tests (such as urine protein tests and eGFR) to detect early signs of kidney disease.
By staying proactive with blood sugar management, eating well, exercising, and following your doctor’s recommendations, you can protect your vital organs and live a healthier, longer life. Small daily choices can make a big impact on preventing diabetes-related complications.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Your Eyes, Heart, and Kidneys from High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar can have serious and lasting effects on your eyes, heart, and kidneys. The damage often develops silently over time, meaning you may not notice symptoms until complications become severe. If left unmanaged, hyperglycemia can lead to diabetic retinopathy and vision loss, heart disease, high blood pressure, and kidney failure. However, the good news is that these risks can be reduced with proper blood sugar management and a healthy lifestyle.
By making smart choices—such as following a balanced diet, staying active, monitoring your blood sugar levels, and keeping up with regular doctor visits—you can help prevent these complications and maintain better overall health. Early intervention is key to protecting your vital organs and improving your quality of life.
If you have diabetes or are at risk, don’t wait until symptoms appear. Start taking action today to control your blood sugar and safeguard your long-term health. Your eyes, heart, and kidneys will thank you!